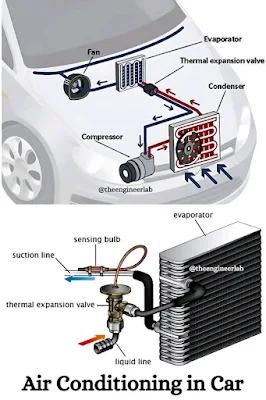
An air conditioning (AC) system is designed to control temperature, humidity, and air quality. It achieves this through a cycle of heat absorption and release using five main components: the compressor, condenser, thermal expansion valve, evaporator, and fan.
1. Compressor:
Often called the heart of the AC system, the compressor compresses the low-pressure refrigerant gas into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This is essential to circulate the refrigerant through the system.
2. Condenser:
Located outside the building, the condenser receives the high-pressure gas from the compressor. As air flows over the condenser coils, the refrigerant loses heat and condenses into a high-pressure liquid. This process releases the absorbed heat into the outside air.
3. Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV):
This small but critical component regulates the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. As the high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the valve, it expands and cools rapidly, becoming a low-pressure, low-temperature mixture.
4. Evaporator:
Found inside the indoor unit, the evaporator coil allows the cold refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air. A fan blows warm air over the coil, and the refrigerant inside absorbs the heat, cooling the air. As the refrigerant heats up, it evaporates back into a gas.
5. Fan:
AC systems typically have two fans—one in the indoor unit and one in the outdoor unit. The indoor fan circulates room air across the evaporator coil and back into the room. The outdoor fan blows air over the condenser coil to help expel heat from the refrigerant.



No comments:
Post a Comment